Saif
Senior Member
- Joined
- Jan 24, 2024
- Messages
- 16,880
- Likes
- 8,153
- Nation

- Residence

- Axis Group


Dhaka ready to work with int'l community for Rohingya repatriation: CA
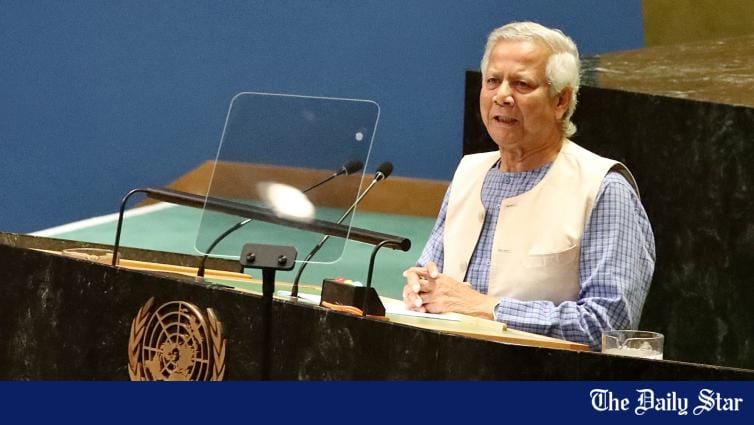
Chief Adviser Professor Muhammad Yunus today said Bangladesh is ready to work with the international community to create an environment for a dignified and sustainable return of the Rohingyas to their homeland in Myanmar
Dhaka ready to work with int'l community for Rohingya repatriation: CA

Photo: PID
Chief Adviser Professor Muhammad Yunus today said Bangladesh is ready to work with the international community to create an environment for a dignified and sustainable return of the Rohingyas to their homeland in Myanmar.
"Looking at the evolving ground situation in Myanmar, Bangladesh is ready to work with the international community to create an environment for dignified and sustainable return of the Rohingyas to their homeland," he said while addressing the 79th session of the United Nations General Assembly (UNGA) in New York.
The chief adviser said seven years on, Bangladesh has been hosting over 1.2 million Rohingyas on humanitarian ground, incurring significant social-economic-environmental costs.
The protracted crisis in Myanmar also poses growing risks with national and regional security implications for Bangladesh, both traditional and non-traditional security challenges, he said.
"We remain committed to supporting the forcibly displaced Rohingyas from Myanmar in Bangladesh. We need continued support of the international community towards the Rohingyas in carrying out the humanitarian operations and their sustainable repatriation," Prof Yunus said.
He said equally important is to ensure justice for the grave human rights violations committed against the Rohingyas, through the ongoing accountability processes in the ICJ and the ICC.
"We recognise and appreciate the efforts of the Secretary General and the United Nations system in creating a conducive environment for Rohingyas so that they can lead a free and dignified life," he said.
The Nobel Laureate said it requires creating pathways for the Rohingyas to return to their ancestral home in Rakhine State, with safety and rights.
Photo: PID
Chief Adviser Professor Muhammad Yunus today said Bangladesh is ready to work with the international community to create an environment for a dignified and sustainable return of the Rohingyas to their homeland in Myanmar.
"Looking at the evolving ground situation in Myanmar, Bangladesh is ready to work with the international community to create an environment for dignified and sustainable return of the Rohingyas to their homeland," he said while addressing the 79th session of the United Nations General Assembly (UNGA) in New York.
The chief adviser said seven years on, Bangladesh has been hosting over 1.2 million Rohingyas on humanitarian ground, incurring significant social-economic-environmental costs.
The protracted crisis in Myanmar also poses growing risks with national and regional security implications for Bangladesh, both traditional and non-traditional security challenges, he said.
"We remain committed to supporting the forcibly displaced Rohingyas from Myanmar in Bangladesh. We need continued support of the international community towards the Rohingyas in carrying out the humanitarian operations and their sustainable repatriation," Prof Yunus said.
He said equally important is to ensure justice for the grave human rights violations committed against the Rohingyas, through the ongoing accountability processes in the ICJ and the ICC.
"We recognise and appreciate the efforts of the Secretary General and the United Nations system in creating a conducive environment for Rohingyas so that they can lead a free and dignified life," he said.
The Nobel Laureate said it requires creating pathways for the Rohingyas to return to their ancestral home in Rakhine State, with safety and rights.