Saif
Senior Member
- Joined
- Jan 24, 2024
- Messages
- 16,447
- Likes
- 8,111
- Nation

- Residence

- Axis Group

Are we ready for Bangladesh 2.0?

We must commit ourselves to work with women, girls, youth, the discriminated, and the marginalised to build their agency and voice in Bangladesh 2.0. PHOTO: AFP
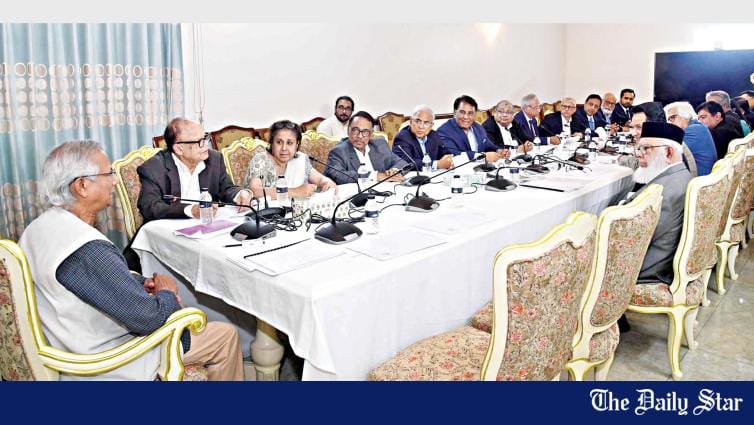
What just happened in Bangladesh is a revolution led and staged by students with people's support. In this historical moment when Gen Z and reformists are driving Bangladesh, I feel charged and would like to reflect on the call made by Dr Muhammad Yunus for people to come forward and work with him. The Yunus-led interim government along with the student leaders have the task for reform and the establishment of justice cut out for them. So let us take a step in the direction of our action and commitment to materialise this agenda.
Should we call for a new social contract—an agreement among individuals within a social group to abide by rules and laws for collective good—that reflects inclusion and equity? Are we ready to decolonise our minds and refrain from the "fear narrative" across all levels? Can we commit to stop celebrating violence in all possible narratives? If not, can there be a change until we shed old habits and work on our sense of responsible citizenship, moral values, and integrity?
Are we ready to stop discriminating based on gender, class, and caste, responding to the movement's call for an end to discrimination? Will we refrain from oppressing the marginalised? Will society commit to ending patriarchy? Can we commit to ending abuse due to structural causes as well as child abuse, child marriage, domestic violence, harassment, and sexual abuse perpetrated by individuals in both private and public spaces? Would this be possible in a society where 51 percent of girls in the age group of 15-18 years in Bangladesh are still being married off?
One way to address these will be by taking legal measures and bringing systemic change. However, these efforts will fail if we do not work to end socially acceptable harmful practices, sustained by society. Arguments put forward for harmful practices have always been about the safety and security of the girls and women in society. Did anyone ask if they need protectors or would rather opt for the end of male dominance? Are we ready to acknowledge the toxic traits of the oppressors that have inadvertently infected everyone even though the nation collectively hate them? I, however, understand that patriarchy and oppression by the powerful will take time to wear off.
Also, are we willing to restrain from arrogance and self-promotion, self-interest, and power aggrandizement? Experts have repeatedly stated that one of the reasons for the fall of the autocrat is her arrogance that grew from a sense of power over others and intolerance to dissent.
Are we ready not to impose our beliefs and thoughts on others and instead work on universal values? Are we ready to rise above our comfort zones and sit at the same table with those with opposing views to be truly inclusive? Can we agree not to force our decisions on children, and respect women and girls? Will we commit not to grab power, business, land, and property? Youth should be aware when the elders try to rationalise these practices as something necessary to secure their future.
We believe malpractice and exploitation cannot be the foundation of any stable or sustainable future. However, can we expect corporate actors to move away from extractive and exploitative practices and engage in business interests with the environment, ecology, climate change, and climate justice in mind? Will they commit to the transition from fossil fuels to green growth and invest as necessary to make that critical change? Youth engagement in climate justice is increasingly vital for fostering lasting change, particularly in Bangladesh, where recent political shifts have amplified the voices of young people. Their collective demands include accountability and transparency in the management of climate funds, alongside the eradication of corruption in environmental projects. As we rebuild the country, strong advocacy for a green economic recovery emphasising sustainable job creation in renewable energy and eco-friendly industries is needed. Addressing the challenges youth face at the grassroots level is essential, particularly in the context of climate justice. The actions today will shape the future.
No one is safe until all can participate and enjoy their entitlements. Therefore, society's agenda should be: how will we make everyone feel welcome and comfortable to share their thoughts and be heard as a mark of us respecting knowledge leadership, community, women, and youth leadership? Can we be connected to people, thoughts, ambitions, ideas, approaches, and energy in a way that has not been the case before?
Can we commit ourselves to work with women, girls, youth, the discriminated, and the marginalised to build their agency and voice in Bangladesh 2.0?
Farah Kabir is the country director of ActionAid Bangladesh.
We must commit ourselves to work with women, girls, youth, the discriminated, and the marginalised to build their agency and voice in Bangladesh 2.0. PHOTO: AFP
What just happened in Bangladesh is a revolution led and staged by students with people's support. In this historical moment when Gen Z and reformists are driving Bangladesh, I feel charged and would like to reflect on the call made by Dr Muhammad Yunus for people to come forward and work with him. The Yunus-led interim government along with the student leaders have the task for reform and the establishment of justice cut out for them. So let us take a step in the direction of our action and commitment to materialise this agenda.
Should we call for a new social contract—an agreement among individuals within a social group to abide by rules and laws for collective good—that reflects inclusion and equity? Are we ready to decolonise our minds and refrain from the "fear narrative" across all levels? Can we commit to stop celebrating violence in all possible narratives? If not, can there be a change until we shed old habits and work on our sense of responsible citizenship, moral values, and integrity?
Are we ready to stop discriminating based on gender, class, and caste, responding to the movement's call for an end to discrimination? Will we refrain from oppressing the marginalised? Will society commit to ending patriarchy? Can we commit to ending abuse due to structural causes as well as child abuse, child marriage, domestic violence, harassment, and sexual abuse perpetrated by individuals in both private and public spaces? Would this be possible in a society where 51 percent of girls in the age group of 15-18 years in Bangladesh are still being married off?
One way to address these will be by taking legal measures and bringing systemic change. However, these efforts will fail if we do not work to end socially acceptable harmful practices, sustained by society. Arguments put forward for harmful practices have always been about the safety and security of the girls and women in society. Did anyone ask if they need protectors or would rather opt for the end of male dominance? Are we ready to acknowledge the toxic traits of the oppressors that have inadvertently infected everyone even though the nation collectively hate them? I, however, understand that patriarchy and oppression by the powerful will take time to wear off.
Also, are we willing to restrain from arrogance and self-promotion, self-interest, and power aggrandizement? Experts have repeatedly stated that one of the reasons for the fall of the autocrat is her arrogance that grew from a sense of power over others and intolerance to dissent.
Are we ready not to impose our beliefs and thoughts on others and instead work on universal values? Are we ready to rise above our comfort zones and sit at the same table with those with opposing views to be truly inclusive? Can we agree not to force our decisions on children, and respect women and girls? Will we commit not to grab power, business, land, and property? Youth should be aware when the elders try to rationalise these practices as something necessary to secure their future.
We believe malpractice and exploitation cannot be the foundation of any stable or sustainable future. However, can we expect corporate actors to move away from extractive and exploitative practices and engage in business interests with the environment, ecology, climate change, and climate justice in mind? Will they commit to the transition from fossil fuels to green growth and invest as necessary to make that critical change? Youth engagement in climate justice is increasingly vital for fostering lasting change, particularly in Bangladesh, where recent political shifts have amplified the voices of young people. Their collective demands include accountability and transparency in the management of climate funds, alongside the eradication of corruption in environmental projects. As we rebuild the country, strong advocacy for a green economic recovery emphasising sustainable job creation in renewable energy and eco-friendly industries is needed. Addressing the challenges youth face at the grassroots level is essential, particularly in the context of climate justice. The actions today will shape the future.
No one is safe until all can participate and enjoy their entitlements. Therefore, society's agenda should be: how will we make everyone feel welcome and comfortable to share their thoughts and be heard as a mark of us respecting knowledge leadership, community, women, and youth leadership? Can we be connected to people, thoughts, ambitions, ideas, approaches, and energy in a way that has not been the case before?
Can we commit ourselves to work with women, girls, youth, the discriminated, and the marginalised to build their agency and voice in Bangladesh 2.0?
Farah Kabir is the country director of ActionAid Bangladesh.